New project targets growing satellite robotics industry
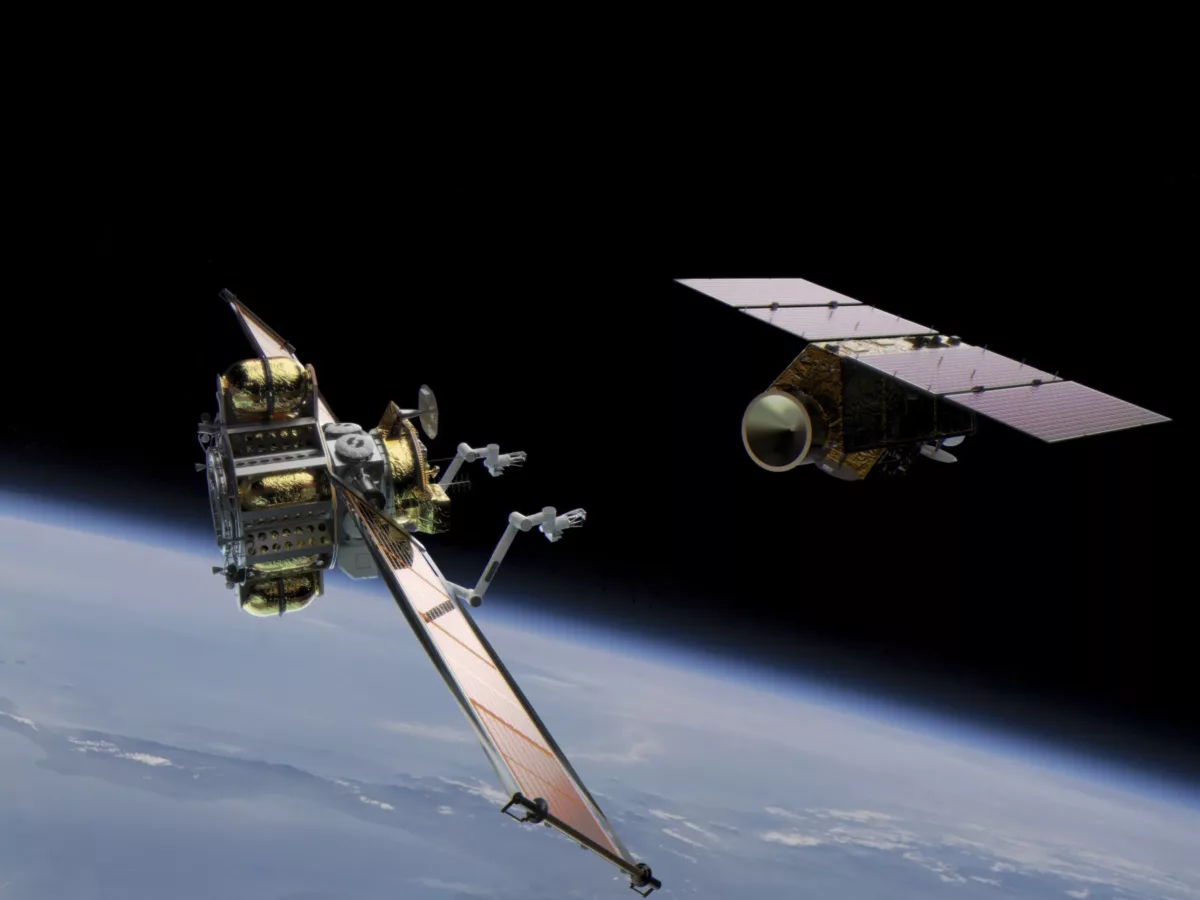

A new $2.3 million project led by University of Sydney, and supported by industry partners Abyss Solutions, ANT61, Space Machines Company, Sperospace and Spiral Blue, focusses on robotic satellite technologies for in-orbit repairs and maintenance.
“With the number of satellites and spacecraft in orbit increasing rapidly, there’s a greater likelihood of malfunctions and collisions,” said SmartSat CRC Chief Executive Officer, Professor Andy Koronios, in a statement on Wednesday.
“Being able to service and upgrade satellites in-situ, thereby extending their lifespans, will be a crucial capability for governments and the private sector alike.
“This project will develop key autonomy technologies needed by the Australian space industry to be competitive in the global ISAM business.”
In a statement on Wednesday, the SmartSat CRC – which is backing the team’s work – said the In-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing (ISAM) project will focus on four areas of research: high-level, AI-driven on-board automation; advanced sensing; a fault-tolerant relative navigation system; and a safe control strategy for reactionless control.
The collective goal of the project is “to build and demonstrate on-ground an end-to-end software stack for these four advanced autonomy technologies into a single working code repository suitable for deployment onto future satellites.”
“This core capability set will enable Australian industry to undertake advanced, fit-for-purpose, autonomous robotic satellite missions to meet commercial, civil and defence needs,” added Dr Xiaofeng Wu, Senior Lecturer in Space Engineering at the University of Sydney.
Wu said ISAM would address the nation’s future sovereign needs, and that the groundwork needed to be laid to compete in a “vital and emerging US$14.3 billion market.”
Picture: credit Space Machines Company
@aumanufacturing Sections
Analysis and Commentary Awards Defence Manufacturing News Podcast Technology Videos