Sparc Hydrogen reveals details of photocatalytic hydrogen pilot plant
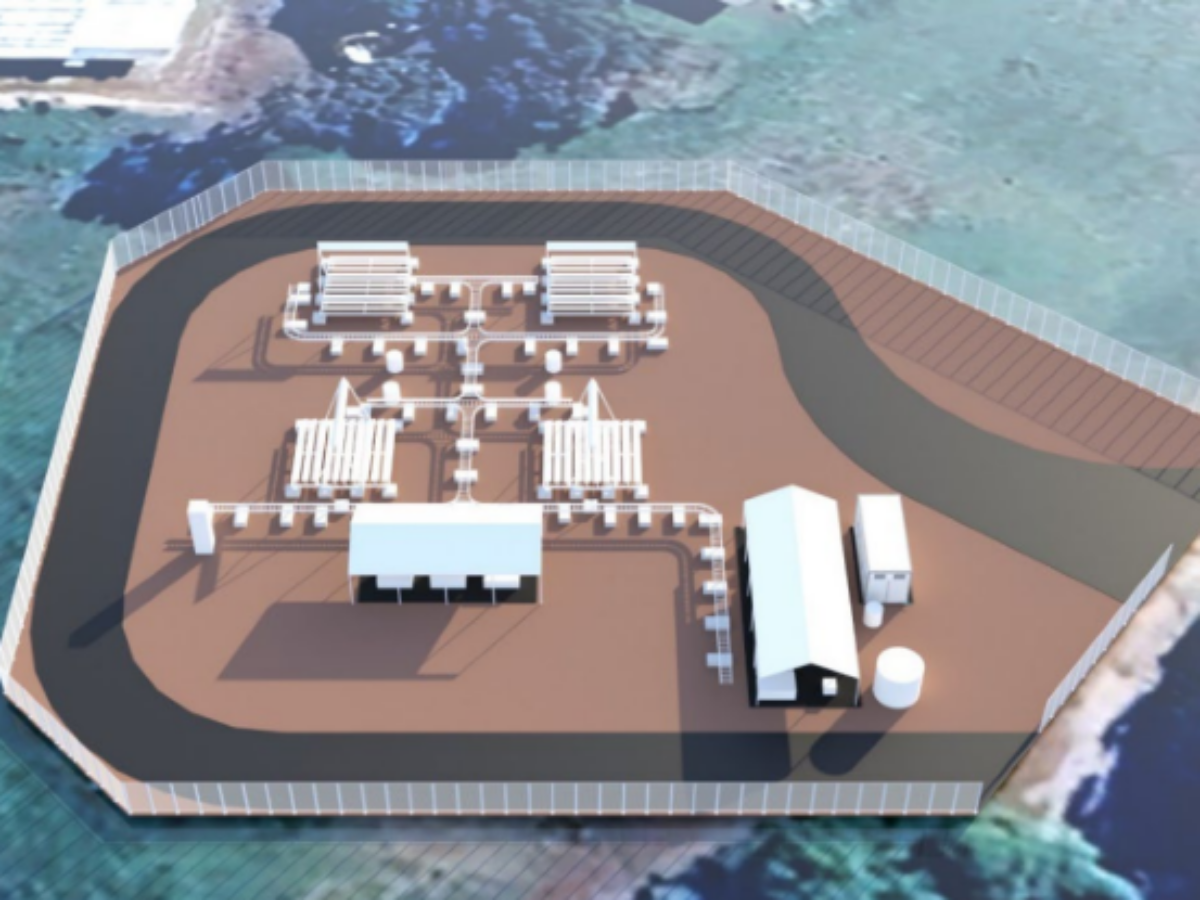

Sparc Hydrogen has significantly progressed the design and engineering of a pilot scale photocatalytic water splitting (PWS) reactor to produce green hydrogen at cheaper cost than traditional electrolysis.
The company, a joint venture between Sparc Technologies, Fortescue and the University of Adelaide, has been working collaboratively with a linear Fresnel equipment supplier to ensure the reactor’s compatibility with their solar concentrator design.
Sparc told investors: “The Sparc Hydrogen team has also identified manufacturing capability within Australia to support local construction of the PWS reactors.
“Prototype testing completed at CSIRO Energy Centre provides confidence in the underlying design principles for the pilot scale reactor.”
Sparc said it had made preparations to begin front-end engineering and design (FEED) for the pilot plant with the same engineering firm that led the pre-FEED study completed in Q4 2023.
The FEED study will build on the flowsheet developed during the pre-FEED, which included four linear Fresnel modules within an end-to-end green hydrogen production system (pictured).
“The pilot plant will allow Sparc Hydrogen to independently and concurrently test different reactor designs and photocatalyst materials.
“Sparc Hydrogen is not aware of any similar facilities developed for testing photocatalytic water splitting under concentrated solar conditions around the world.”
During the latest quarter Sparc signed a collaboration Framework Agreement with Shinshu University of Nagano, Japan regarding photocatalyst supply.
The CFA envisages the use of photocatalysts developed by Shinshu in solar reactors developed by Sparc Hydrogen.
Shinshu University is a key participant in Japan’s ARPChem project, a collaborative research initiative backed by Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), which has previously demonstrated the feasibility of producing hydrogen through photocatalytic water splitting.
Participants in ARPChem include INPEX Corporation, JX Nippon Mining & Metals Corporation, Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd., Dexerials Corporation, Toray Industries Inc., Toyota Motor Corporation, Nippon Steel Corporation, Furuya Metal Co., Ltd., Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. and Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation.
The University of Adelaide has provided Sparc Hydrogen with in-principle support to locate the pilot plant at its Roseworthy Campus, 50km north of the Adelaide CBD.
Further reading:
Sparc Hydrogen reports success with photocatalytic water splitting
Sparc Hydrogen pilot plant closer with new Japanese partner
Image: Sparc Hydrogen
Topics ARPChem CSIRO Energy Centre Dai Nippon Printing Co. Dexerials Corporation Fortescue Furuya Metal Co. hydrogen Inc. INPEX Corporation JX Nippon Mining & Metals Corporation Ltd. Manufacturing News Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation Mitsui Chemicals New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization Nippon Steel Corporation Shinshu University Sparc Hydrogen Sparc Technologies Technology Toray Industries Inc. Toyota Motor Corporation University of Adelaide
@aumanufacturing Sections
Analysis and Commentary Awards casino reviews Defence Gambling Manufacturing News Online Casino Podcast Technology Videos