Australian needle-free system demonstrates potential for delivering Covid-19 vaccine
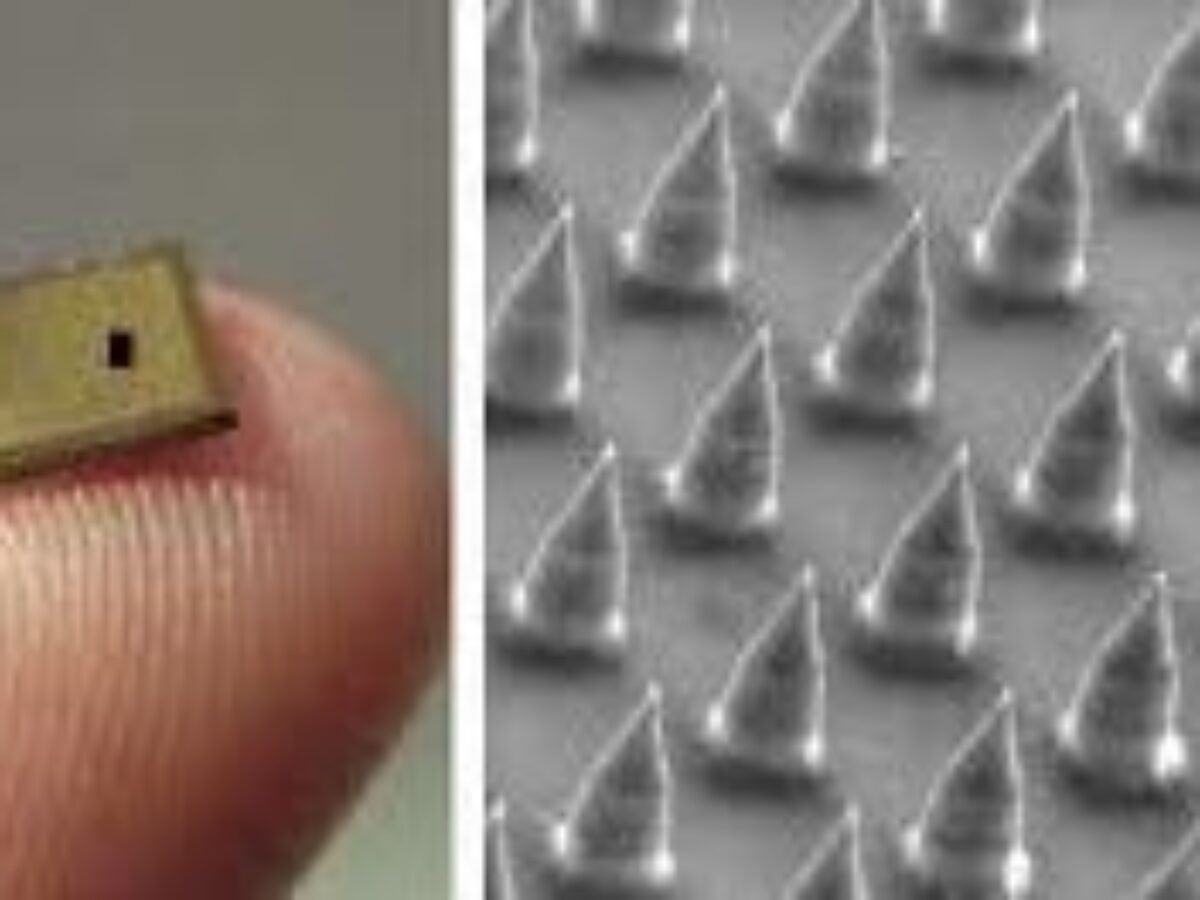
Brisbane-based biotech company Vaxxas has announced evidence their delivery patches show potential in administering Covid-19 vaccine.
Preclinical research published on preprint repository BioRxiv showed “significantly enhanced T-cell and spike-specific antibody responses” versus needle-and-syringe delivery in an animal model, and “complete protection from COVID-19 by a single dose skin patch” in a relevant COVID-19 animal model.
“We designed this research to address the serious on-going need to improve the global vaccination efforts against COVID-19 and future pandemics. Based on our results, we believe that Vaxxas’ HD-MAP could offer a compelling solution that importantly could use less vaccine and potentially could be readily distributed without refrigeration for self-administration,” said principal researcher David A. Muller of The University of Queensland.
“This combination could make the HD-MAP extremely well suited to support the massive need for global population vaccination and, indeed, we believe that HD-MAP offers a superior alternative to conventional needle-and-syringe.”
The research was funded by the Queensland government and Vaxxas, and also showed the vaccine — “a recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, termed HexaPro” — remained stable for at least 30 days at a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius.
Vaxxas was established in 2011 to commercialise its HD-MAP platform, formerly known as “Nanopatch.” This is a needle micro-array concept used to painlessly administer dry vaccines, developed by Professor Mark Kendall and his team.
It operates out of Brisbane’s Translational Research Institute.
Topics Technology
@aumanufacturing Sections
Analysis and Commentary Awards casino reviews Defence Gambling Manufacturing News Online Casino Podcast Technology Videos